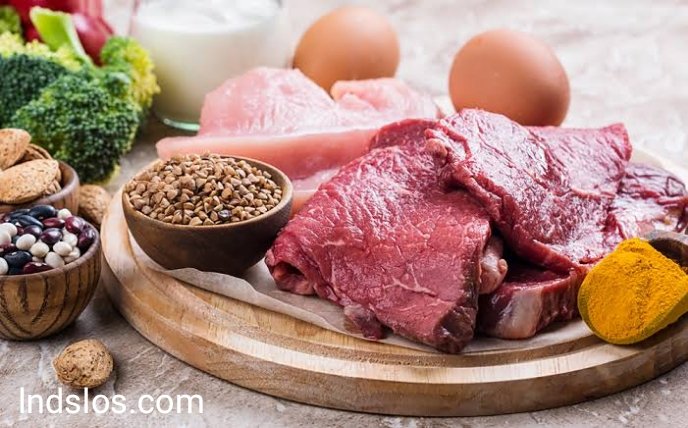

Beef: A Complete Protein and Valuable Source of Essential Nutrients
Beef: A Complete Protein and Valuable Source of Essential Nutrients
Beef is a nutrient-dense food that is a good source of protein, iron, zinc, selenium, riboflavin, niacin, vitamin B6, vitamin B12, phosphorus, pantothenate, magnesium, and potassium. It is also a good source of choline, a nutrient that is important for brain health.
Protein
Beef is a complete protein, which means that it contains all of the essential amino acids that the body needs. Essential amino acids cannot be made by the body, so they must be obtained from food. Protein is important for building and repairing tissues, as well as for maintaining a healthy immune system.
Iron
Beef is a good source of iron, which is an essential mineral for carrying oxygen in the blood. Iron deficiency is a common problem, especially in women. Beef can help to prevent iron deficiency and improve overall health.
Zinc
Beef is a good source of zinc, which is an essential mineral for many bodily functions, including wound healing, immune function, and DNA synthesis. Zinc deficiency is also a common problem, especially in children. Beef can help to prevent zinc deficiency and improve overall health.
Selenium
Beef is a good source of selenium, which is an essential mineral that helps to protect the body against damage from free radicals. Free radicals are unstable molecules that can damage cells and lead to chronic diseases. Selenium deficiency is rare, but it can occur in people who eat a low-selenium diet. Beef can help to prevent selenium deficiency and improve overall health.
Other nutrients

Beef is also a good source of other nutrients, including riboflavin, niacin, vitamin B6, vitamin B12, phosphorus, pantothenate, magnesium, and potassium. These nutrients are important for a variety of bodily functions, including energy production, nerve function, and blood pressure regulation.
How to choose and cook beef
When choosing beef, look for lean cuts that are low in saturated fat. Some good choices include sirloin steak, flank steak, and round steak. When cooking beef, choose healthy cooking methods such as grilling, baking, or broiling. These methods will help to keep the fat content low and the nutrients intact.
Beef as part of a healthy diet
Beef can be a healthy part of a balanced diet. However, it is important to choose lean cuts and to cook them in healthy ways. Beef can be paired with a variety of healthy foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes.
Conclusion
Beef is a nutrient-dense food that is a good source of protein, iron, zinc, selenium, riboflavin, niacin, vitamin B6, vitamin B12, phosphorus, pantothenate, magnesium, and potassium. It can be a healthy part of a balanced diet when it is chosen wisely and cooked in healthy ways.
Keywords: beef, protein, iron, zinc, selenium, riboflavin, niacin, vitamin B6, vitamin B12, phosphorus, pantothenate, magnesium, potassium, lean cuts, grilling, baking, broiling, healthy diet.







Leave a Reply